The blog series "Business Intelligence 101: From Data to Insights" is a beginner's guide to understanding the field of Business Intelligence (BI). The series covers various topics, starting from the basics of BI and moving towards more advanced concepts. The goal of the series is to help readers gain a solid understanding of how BI works and how it can be used to derive insights from data.
Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence (BI) is a collection of methods, tools, and applications that help organizations use data to make informed decisions. BI allows businesses to access new data sources, gain insights, and optimize performance. It provides accurate data for strategic planning, helping businesses stay competitive.
The field of BI encompasses a wide range of topics, including data mining, data warehousing, business analytics, data visualization, and more. These concepts are interconnected and form the foundation of any successful BI strategy.
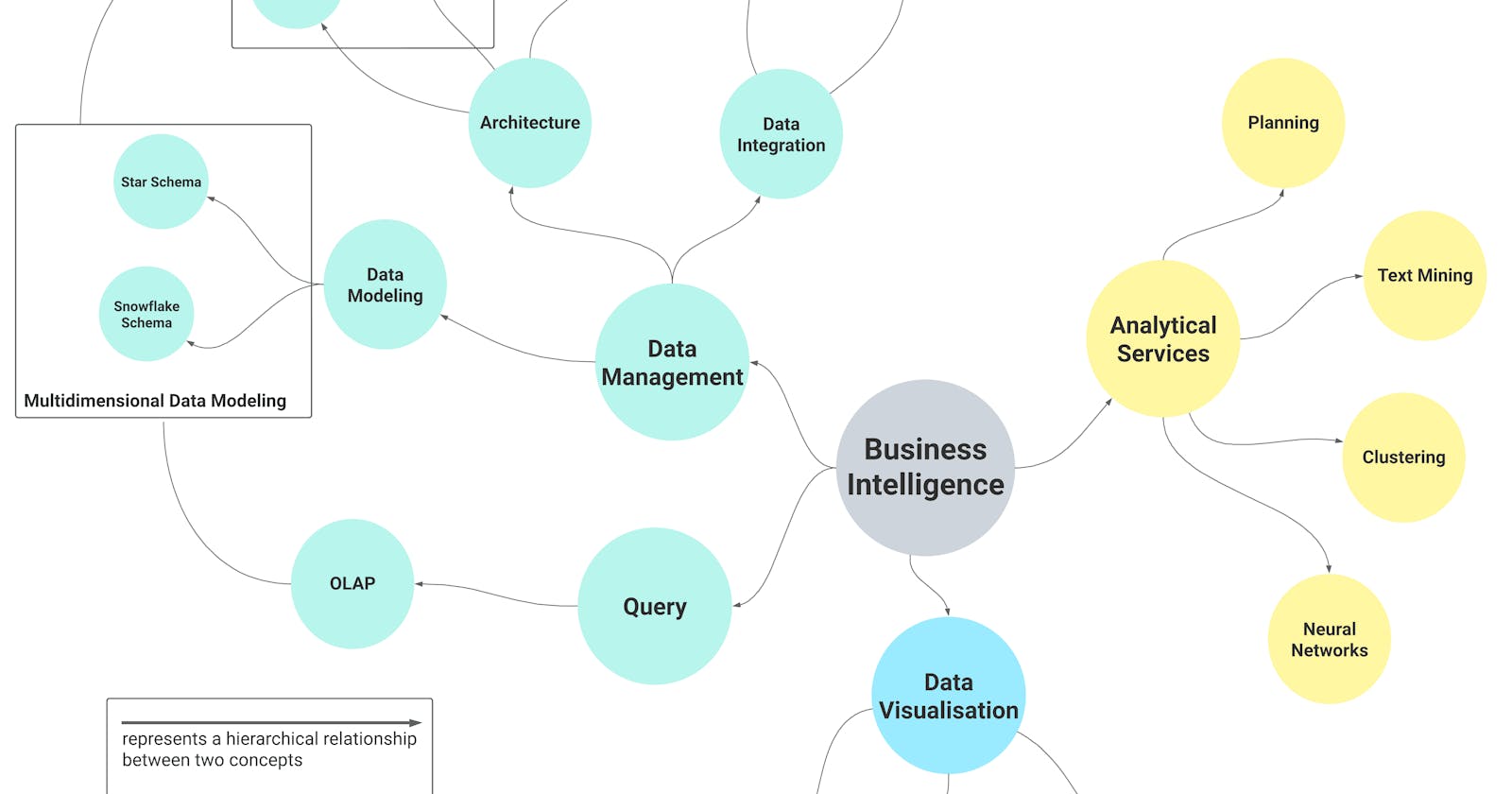
To help organize and visualize the different components of BI, I have created a mind map that highlights some of the key concepts and subtopics that make up this field. By exploring the mind map, you can gain a deeper understanding of the different components of BI and how they fit together to support effective decision-making.

To shed light on how these concepts relate to each other and the principal architecture of Business Intelligence at a high level, the following diagram shows the main components of a BI architecture that connect and encapsulate these concepts.

BI applications
Business Intelligence (BI) applications are used for decision making and can be categorized into three types: strategic, tactical, and operational.
- Strategic BI: provides an overall view of the company's performance from a high-level perspective. It helps organizations make long-term decisions about their goals and objectives.
- Tactical BI: provides more detailed analysis and focuses on short-term decisions.
- Operational BI: is used to measure daily operations.
By understanding these three types of BI applications, organizations can choose the most suitable solutions to meet their needs and make informed decisions.

BI Value
Business Intelligence (BI) can bring significant benefits to organizations in several areas:
- Management processes: BI can help with planning, budgeting, performance monitoring/assessment, process improvement, cost analysis, and optimization.
- Revenue generating processes: BI can assist with customer segmentation, campaign management, channel management, and sales management to generate more revenue.
- Resource consumption processes: BI can optimize product/service development, order management, manufacturing/operations, supply chain, and purchasing to reduce resource consumption.
With these capabilities, BI is a valuable asset for organizations to manage their resources strategically and maximize their revenues.
BI design methodologies
BI design methodologies refer to techniques used to create and execute Business Intelligence (BI) solutions. These methodologies allow organizations to make better decisions and improve operational efficiency. By using appropriate BI design methods, organizations can uncover insights into customer behavior, trends, and opportunities that may have gone unnoticed. They can also create a long-term strategy for their BI initiatives, increasing their chances of success. By adopting BI design methodologies, organizations can maximize their return on investment and ensure their BI solutions meet their desired objectives.

Demand-Driven Methodology
The demand-driven design methodology is a user-focused approach to building a data warehouse for an organization. It starts by understanding the user's needs and works from the bottom up to meet those needs. The process involves identifying specific data marts, building them, and designing fact tables that provide valuable insights. By putting the user's requirements first, the demand-driven design methodology ensures that the data warehouse is efficient and effective in meeting the organization's goals.

Supply-Driven Methodology
Supply-driven data warehouse design methodology is a technique for building a data warehouse that prioritizes data sources. It starts with a top-down analysis of source systems and data flows, in contrast to the demand-driven approach that focuses on the data consumers.

Hybrid Methodology
Hybrid Methodology design combines both top-down and bottom-up approaches to create an effective data warehouse design. Top-down approach considers business users' perspective while the bottom-up approach focuses on the technical details of data sources. By combining both approaches, this methodology aims to achieve the best of both worlds in data warehouse design.

Throughout our blog parts, we have discussed various aspects of Business Intelligence (BI), including its applications, design methodologies, and components. We have also touched on the importance of BI in decision-making processes and how it can add value to an organization's management, revenue generation, and resource consumption processes. In the upcoming blog, we will delve deeper into the world of data management services, specifically focusing on the differences between data warehouse systems and DBMS. Additionally, we will explore the crucial topic of multidimensional data modeling for data warehouses and data marts. By understanding the distinctions between these systems and their respective data modeling techniques, you will be better equipped to optimize your data management processes and make informed decisions for your organization. Stay tuned for an insightful and informative read!